Table of Contents
Introduction:

Personal Health Monitoring(PHM)describes a set of technological artifacts, currently in development and limited use, designed to supplement medical care with health monitoring outside traditional care environments such as hospitals. Applications are in development for nearly every demographic, with many targeting the elderly and chronically ill. This contribution to the FRRIICT repository provides a definition and categorization of PHM based on a review of academic literature addressing the ethical implications of PHM. Controversies and ethical issues unique to the technology are then discussed, focusing on the potential for corporeal surveillance and health categorization of users.
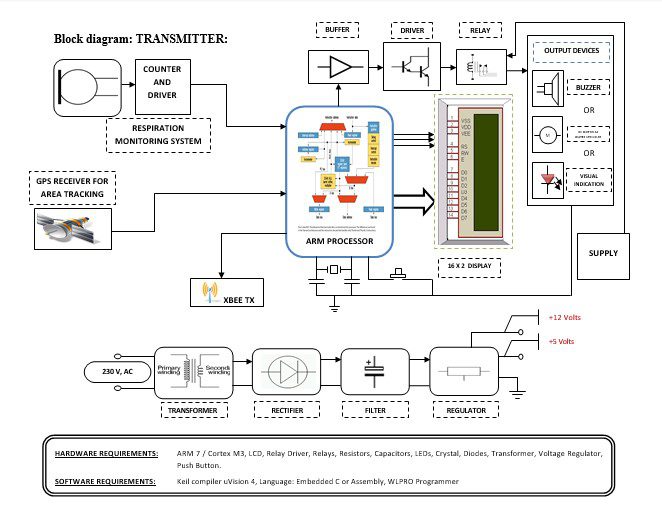

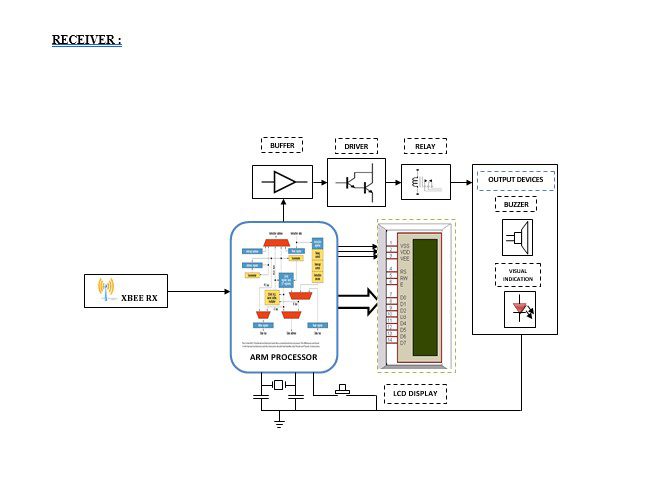

Block diagram explanation :
Power supply unit:
This section needs two voltages viz., +12 V & +5 V, as working voltages. Hence specially designed power supply is constructed to get regulated power supplies.
ARM processor:
ARM is a computer processor-based RISC architecture. A RISC-based computer design approach means ARM processors require significantly fewer transistors than typical processors in average computers. This approach reduces costs, heat, and power use. The low power consumption of ARM processors has made them very popular:
The ARM architecture (32-bit) is the most widely used in mobile devices, and the most popular 32-bit one in embedded systems.
ARM processor features include:
- Load/store architecture.
- An orthogonal instruction set.
- Mostly single-cycle execution.
- A 16×32-bit register
- Enhanced power-saving design.
Zigbee technology:
ZigBee is the name of a specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols using small, low-power digital radios based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for wireless personal area networks (WPANs).
- A very low-cost, low power consumption two-way, wireless communication standard for automation, toys & PC peripherals.
- Low power consumption: 6 months to 5 years battery life for most applications.
- Low cost: At least half the cost of Bluetooth solutions.
- The high density of nodes per network: 250 nodes per network, multiple co-located networks.Data rate requirements: Few bits to 250kbps sufficient.
Buffers:
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
Drivers:
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relays:
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Indicator:
This stage provides a visual indication of which relay is actuated and deactivated, by glowing respective LED or Buzzer.
Methodology:
The project consists of a transmitter for each of the patients and a single receiver in the doctor’s monitoring room.
The patient circuit consists of the sensor unit, controller, and transmitter. If any variation occurs in the patient sensor will indicate. The signal from the sensor is given to the controller. Then the controller will indicate the patient requirement via display and the same information is transmitted via Zigbee also send the coordinates read from GPS for location identification.
On the doctor’s end, the receiver is common for all the transmitted signals. The signal is received in the receiver via ZigBee. The received signal is given to the ARM to present corresponding voice information to indicate exactly the patient’s requirement. GPS
Advantages:
- Hospitals in monitoring the Heart Beat and Temperature continually.
- Any abnormality felt by the patient is indicated by a voice signal.
- The patients can be analyzed by doctors in any part of the hospital wherever they are.
- Thus it reduces the workload of nurses and also gives more accurate results.
- The patient-staff ratio is very low, so these kinds of advanced equipment are necessary.
Disadvantages:
One-time investment cost.
Applications:
1. Area monitoring
2. Health care monitoring
3. Forest fire detection
4. Landslide detection
5. Industrial monitoring
6. Natural disaster prevention