Table of Contents
Introduction:


The word robot originated from the Czech word robot, meaning work. A definition used by the robot institute of America is: “A robot is a programmable multifunction manipulator designed to move material, parts, tools, or specialized devices through variable programmed motions for the performance of a variety of tasks”. In this highly developing society, time and manpower are critical constraints for the completion of tasks. Automation is playing an important role to save human efforts in most of the regular and frequently carried work. The idea that machines can begin to imitate human actions, even in ways we have not thought of, the main motives for the creation of robots have been very practical. First, as the modern industry has become more complex, there has been a growing need for getting work done in environments that are dangerous for humans. As an example, work in a nuclear reactor plant often requires contact with radioactive materials. Second, as robots became more advanced and less expensive, they are being set up in industry situations where working conditions are not so much dangerous as unpleasant for various reasons. These situations typically involve high degrees of the following: – Heat, Noise, Poisonous gases, Risk of injury by machines, Monotonous, boring work. Robots have already taken over several such unpleasant jobs in the industry- welding in automobile factories, which involves heat, noise, and heavy exertion. Robots are obedient, untiring, and precision welders. Simple robots do many routine jobs in the industry. Pick and place robots are useful in simple assembly operations such as stuffing printed circuit boards and loading and unloading parts from machines
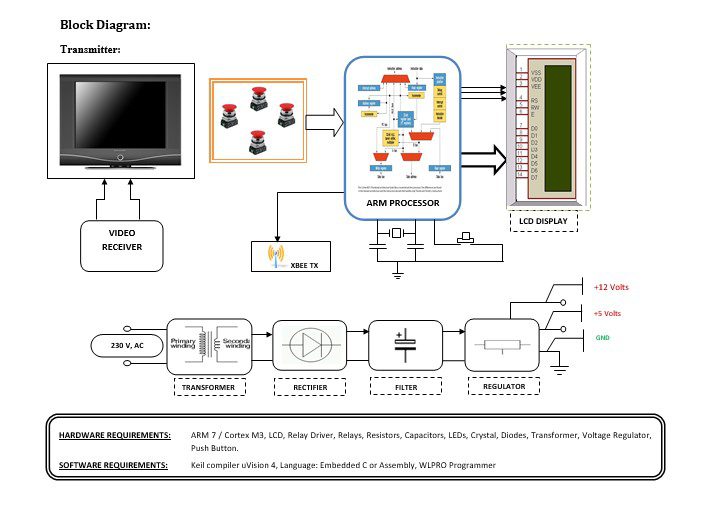

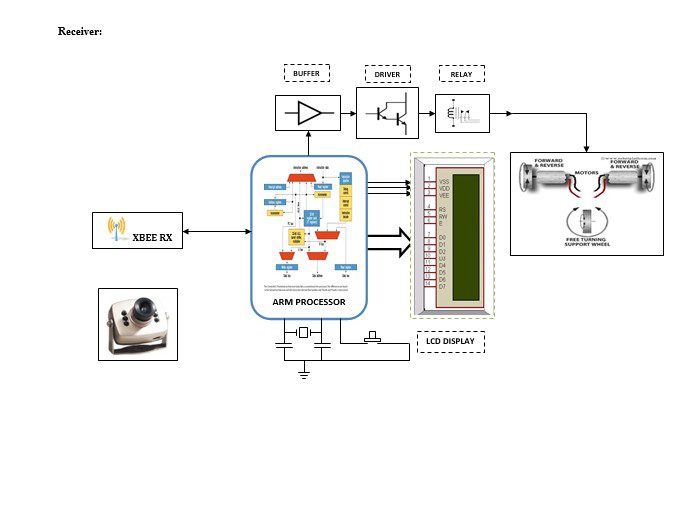

Block diagram explanation:
Power supply unit:
As the whole RF Transmitter Unit goes with the vehicle, its power supply must be kept compact and compatible with all kinds of vehicles and their power generators.
Arm 7:
The heart of the system is the microcontroller which will access the data. In our project, ARM7 is used. The ARM7 which we used for our project is LPC2148 (PHILLIPS) ARM7 is a high-performance, low-cost, low-power consumption RISC processor. For a variety of areas, such as embedded control, multimedia, DSP, and mobile applications, ARM architecture is the first RISC microprocessor designed for the low-budget market. The embedded operating system will be subject to certain restrictions. But because of its low price, reliability, and other factors, it is widely used in various industrial controllers.
Zigbee technology:
ZigBee is the name of a specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols using small, low-power digital radios based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for wireless personal area networks (WPANs).
- A very low-cost, low power consumption two-way, wireless communication standard for automation, toys & PC peripherals.
- Low power consumption: 6 months to 5 years battery life for most applications.
- Low cost: At least half the cost of Bluetooth solutions.
- The high density of nodes per network: 250 nodes per network, multiple co-located networks Data rate requirements: Few bits to 250kbps sufficient.
Buffer:
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
Driver:
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relay:
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Methodology:
A block diagram which is shown above is divided into two parts that are transmitter and receiver. The transmitter part is which is in the control room which can be controlled from a remote area using ZIGBEE as a communication protocol. The person at the transmitting end controls the robot of the remote areas using key inputs along with that he can view any mishandling in the industries like damages in pipes gas leakage, etc.. using the camera.
Advantages:
1. Quality:
Industrial automated robots can dramatically improve product quality. Applications are performed with precision and high repeatability every time. This level of consistency can be hard to achieve any other way.
2. Production:
With robots, throughput speeds increase, which directly impacts production. Because an automated robot can work at a constant speed without pausing for breaks, sleep, or vacations, it has the potential to produce more than a human worker.
3. Safety:
Robots increase workplace safety. Workers are moved to supervisory roles where they no longer have to perform dangerous applications in hazardous settings.
4. Savings:
Improved worker safety leads to financial savings. There are fewer healthcare and insurance concerns for employers. Automated robots also offer untiring performance which saves valuable time. Their movements are always exact, minimizing material waste.
Disadvantages:
1. Expense:
The initial investment to integrate automated robotics into your business is significant, especially when business owners are limiting their purchases to new robotic equipment. The cost of robotic automation should be calculated in light of a business’ greater financial budget. Regular maintenance needs can have a financial toll as well.
2. ROI:
Incorporating industrial robots does not guarantee results. Without planning, companies can have difficulty achieving their goals.
3. Expertise:
Employees will require a training program and interact with the new robotic equipment. This normally takes time and financial output.
4. Safety:
Robots may protect workers from some hazards, but in the meantime, their very presence can create other safety problems. These new dangers must be taken into consideration.
Applications:
- Aerospace
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Health
- Nuclear
- Textile
- Lab automation
- Underwater surveying
- Surveillance and guard duty
- Navigation systems
- Firefighting
- Household robot




