Table of Contents
Introduction:

Electricity is an extremely handy and useful form of energy. It plays an ever-growing role in our modern industrialized society. The electrical power systems are highly non-linear, extremely huge, and complex networks. Such electric power systems are unified for economic benefits, increased reliability, and operational advantages. They are one of the most significant elements of both national and global infrastructure, and when these systems collapse it leads to major direct and indirect impacts on the economy and national security. A power system consists of components such as generators, lines, transformers, loads, switches, and compensators. However, widely dispersed power sources and loads are the general configuration of modern power systems. Electric power systems can be divided into two sub-systems, namely, transmission systems and distribution systems. The main process of a transmission system is to transfer electric power from electric generators to the customer area, whereas a distribution system provides an ultimate link between high-voltage transmission systems and consumer services. In other words, the power is distributed to different customers from the distribution system through feeders, distributors, and service mains. Supplying electricity to consumers necessitates power generation, transmission, and distribution. Initially, electric power is generated by using electric generators such as nuclear power generators, thermal power generators, and hydraulic power generators and then transmitted through transmission systems using high voltage. Power departs from the generator and enters into a transmission substation, where huge transformers convert the generator’s voltage to extremely high voltages (155kV to 765 kV) for long-distance (up to about 300 miles) transmission. Then, the voltage level is reduced using transformers and power is transferred to customers through electric power distribution systems. Power starts from the transmission grid at distribution substations where the voltage is stepped-down (typically to less than 10kV) and carried by smaller distribution lines to supply commercial, residential, and industrial users.
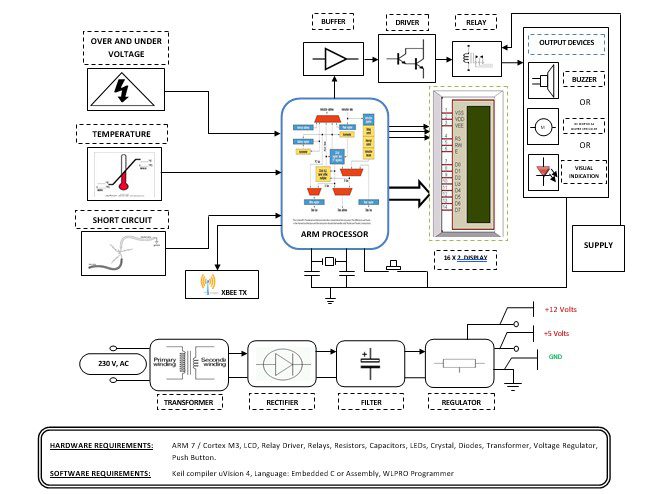

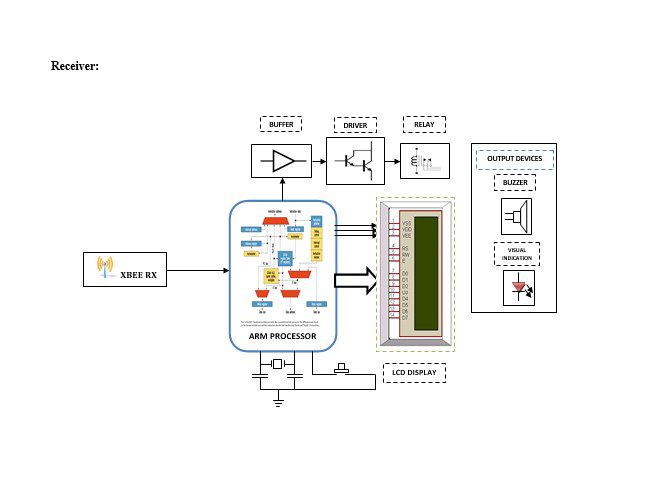

Block diagram explanation
Power supply unit
This section needs two voltages viz., +12 V & +5 V, as working voltages. Hence specially designed power supply is constructed to get regulated power supplies.
Over voltage and under voltage:
When the voltage in a circuit or part of it is raised above its upper design limit, this is known as overvoltage.
ARM processor
ARM is a computer processor-based RISC architecture. A RISC-based computer design approach means ARM processors require significantly fewer transistors than typical processors in average computers. This approach reduces costs, heat, and power use. The low power consumption of ARM processors has made them very popular:
The ARM architecture (32-bit) is the most widely used in mobile devices, and the most popular 32-bit one in embedded systems.
Zigbee Technology
ZigBee is a specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks built from small, low-power digital radios. ZigBee is based on an IEEE 802.15 standard. Though low-powered, ZigBee devices can transmit data over long distances by passing data through intermediate devices to reach more distant ones, creating a mesh network
Buffers
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
Drivers
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relays
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Buzzer:
A buzzer or beeper is an audio signaling device, which may be mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Typical uses of buzzers and beepers include alarm devices, timers, and confirmation of user input such as a mouse click or keystroke.
DC motor:
A DC motor relies on the fact that magnet poles repel and unlike magnetic poles attracts each other. A coil of wire with a current running through it generates an electromagnetic field aligned with the center of the coil. By switching the current on or off in a coil its magnetic field can be switched on or off or by switching the direction of the current in the coil the direction of the generated magnetic field can be switched 180°.
Indicator:
This stage provides a visual indication of which relay is actuated and deactivated, by glowing respective LED or Buzzer.
Methodology:
This project is developed to monitor and control the substation system for the electricity board and to send the information about the variation in the substation to the Head Office using Zigbee. This project contains three sensors for over-voltage and under-voltage detection, temperature detection, and short-circuit detection. After sensing that parameter depending on the scenario the ARM controller will take appropriate action. The main modules in this project are Sensors (over voltage and under voltage detection, temperature sensor, and short circuit sensor), ARM controller unit with LCD, and output device.
This transmitter model is placed in Substation and the receiver will there in Head Office. This model has three Sensors as an input device to substations and depending on the parameter measured the controller will take appropriate action. The same information will be sent to the Head Office via Zigbee. The receiver will activate the outputs to indicate a sensor has detected a signal the Head Office has to take appropriate action.
Advantages:
1. Cost efficiency.
2. In this project losses are Minimal.
3. This project can implement for the Security of supply.
Disadvantages:
1. The electricity network only (not gas) concerns both distribution and transmission levels.
2. It increases the cost whereas digital systems reduce the cost of the system.
Applications:
- This system can be implemented in industries.
- This system can be implanted in schools, colleges, companies, etc…
- This system can be used to monitor and control the home appliances




