Table of Contents
Introduction:

The project presented here is a novel approach to vehicle navigation & safety implementation. As the title suggests, the project is aimed at automatically sensing the areas/zone “Curve Zone” or “Accident Zone”.
In convention, these special zones or areas are indicated at the roadside on a pillar or road sign pole.
Even though these are meant for the safety of the vehicles traveling and also for the general public, it is hardly practiced by vehicle drivers. As a result, making the whole concept of displaying warning signs and messages on the roadside boards is meaningless.
To provide a better alternative, one can develop a system that will automatically sense such traffic signs automatically and accordingly inform the drivers and also assist them in controlling the vehicle voluntarily or forcibly. All in all, resulting in a very effective and fail-proof system to provide traffic regulation, safety, and convenience to the people.
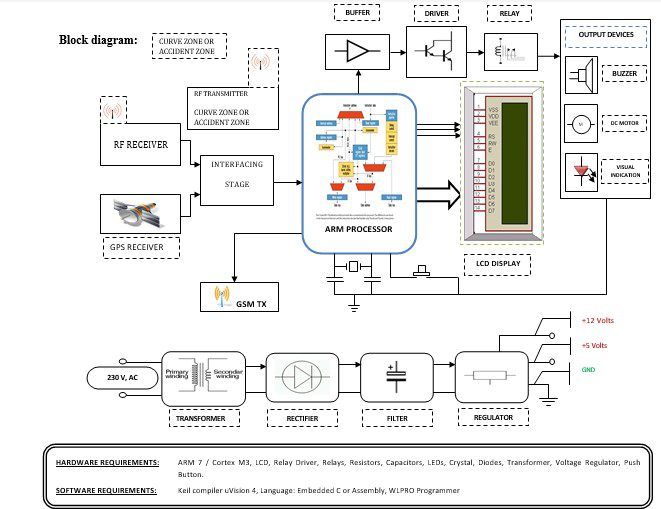

Block diagram explanation:
Power supply unit:
This section needs two voltages viz., +12 V & +5 V, as working voltages. Hence specially designed power supply is constructed to get regulated power supplies.
GPS module:
This is a GPS Receiver (5V Serial) with high gain having 4 Pin 2.54mm pitch strip. The third-generation POT (Patch Antenna on Top) is used by the receiver for the GPS module. It can be interfaced with normal 5V ARM7 with the help of the in-built 3V-5V converter. The interfacing is made easier with the help of a low pin count (4-pin) strip. The 4 Pins are 5V, TX, RX, and GND. This standalone 5V GPS Module does not require external components. It consists of an internal RTC Back up battery and can be directly connected to the USART of the ARM7.
The current date, time, longitude, latitude, altitude, speed, and travel direction / heading among other data, are provided by the module and can be used in many applications including navigation, fleet management, tracking systems, mapping, and robotics. The module can support up to 51 channels. The GPS solution enables small form factor devices which deliver major advancements in GPS performance, accuracy, integration, computing power, and flexibility. They are used to simplify the embedded system integration process.
GSM:
GSM Shield (SIM 900a): The SIM900 which is a complete Quad-band GSM/GPRS solution comes in a SMT module that can be embedded in customer applications. Featuring an industry-standard interface, the SIM900 delivers GSM/GPRS 850/900/1800/1900MHz performance for Data, voice, SMS, and Fax in a small form factor and with low power consumption. SIM900 can fit almost all the space requirements in the M2M application with dimensions of 24mm x 24mm x 3 mm. SIM900 is designed with a very powerful single-chip processor integrating AMR926EJ-S core. Quad-band GSM/GPRS module with a size of 24mmx24mmx3mm, SMT type suit for customer application, An embedded Powerful TCP/IP protocol stack Based upon the mature and field-proven platform, backed up by our support service, from definition to design and production.
NOTE: Modem may change.
ARM processor:
ARM is a computer processor-based RISC architecture. A RISC-based computer design approach means ARM processors require significantly fewer transistors than typical processors in average computers. This approach reduces costs, heat, and power use. The low power consumption of ARM processors has made them very popular:
The ARM architecture (32-bit) is the most widely used in mobile devices, and the most popular 32-bit one in embedded systems.
ARM processor features include:
- Load/store architecture.
- An orthogonal instruction set.
- Mostly single-cycle execution.
- A 16×32-bit register
- Enhanced power-saving design.
Buffers:
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
Drivers:
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relays:
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Indicator:
This stage provides a visual indication of which relay is actuated and deactivated, by glowing respective LED or Buzzer.
RF transmitter:
This is a 2-channel Radio Frequency Transmitter specially tuned with its RF Receiver part in carrier frequency. Each zone is set with one channel and transmits its presence to the moving vehicle’s RF Receiver unit.
RF receiver:
This is also a 2-channel RF Receiver specially tuned with its counterpart RF Transmitter in carrier frequency. When the vehicle enters any zone that zones RF signals are received by this unit. Thus depending upon the channel signals it receives from the transmitting end the channel output of the RF Receiver goes HIGH. This HIGH signal is fed to the ARM7 chip through Buffer & Driver and Switching stage for further processing.
Methodology:
This System GPS Based Sensitive Area Locator is with Automatic Control system that works like this. Each monitoring zones are fitted with RF Transmitter units with a unique Identity Code. All the vehicles must be fitted with RF receivers and respective circuitry on their vehicle’s number plate. The display will be fitted on the dashboard for a visual representation of the alert messages sent by respective zone Transmitters.
When a vehicle with 70 Kmph speed enters the Curve zone, it receives the alert message ”Curve Zone, Please go slowly. Speed limit is 30 Kmph”. Also, the receiver checks the speed limit of the vehicle and found above 30 kmph then reduces it until crosses the Curve Zone area. If any accident happens then GPS reads the coordinates of the accident location and then send it through GSM near the police station or concerned peoples.
Advantages:
- The user can determine their location.
- The information provided is spatially related to the user’s location.
- The user is offered dynamic or two-way interaction with the location information or content.
- This application is very useful for any kind of vehicle.
- This application is easy to install and easy to operate.
- Manpower can be saved by implementing auto-detecting circuits.
- More reliable than manual Operation.
Disadvantages:
- The only thing that is clear about constitutional protections for location-based service information is the lack of clarity.
Applications:
1. Navigation.
2.Surveying.
3.Business process.
4.Warehouse and routing.
5.The project is used to secure and avoid road accidents.
6.It can be used as part of the automation of s or Public Transportation.
7.This system is used to trace the culprit vehicles by police persons.
8.This system can be used for ‘timekeeping’ purposes in public transportation, such as departure & arrival timings, the number of rotations each vehicle turned, etc.