Table of Contents
Introduction:
Electricity networks are currently mainly based on technology that was developed for one-way energy flows from large, centralized, fully controllable power plants to more or less passive customers at the receiving end of the network (Figure 1). Electric power is a fundamental utility in modern society. The rise in variable and distributed generation, under-investment in transmission infrastructure, the increase in electric load, more power outages, and the demand for increased reliability and power quality are all fundamental drivers for the Smart Grid. “Smarter” grids have the potential to assist with the integration of variable-output renewable and distributed power sources, provide high power quality to all customers, facilitate active participation of users in electricity markets, increase overall energy efficiency, facilitate mass electrification of transport, and optimize investment in grid infrastructure. The term “Smart Grid” refers to both transmission and distribution grids, despite the different technologies that will be utilized in future “smart” transmission and distribution. Common for the two, is that there will be no fundamental change to the traditional “copper and iron” infrastructure used to transport electricity. Rather, the Smart Grid will materialize through strategic implants of monitoring, control, and communication systems, within and alongside the existing electricity grid. The Smart Grid term is widely used and misused. Because the term encompasses a wide range of issues, providing a concise, precise definition is not simple. Indeed, the utilities themselves find it challenging to understand what the Smart Grid is all about.
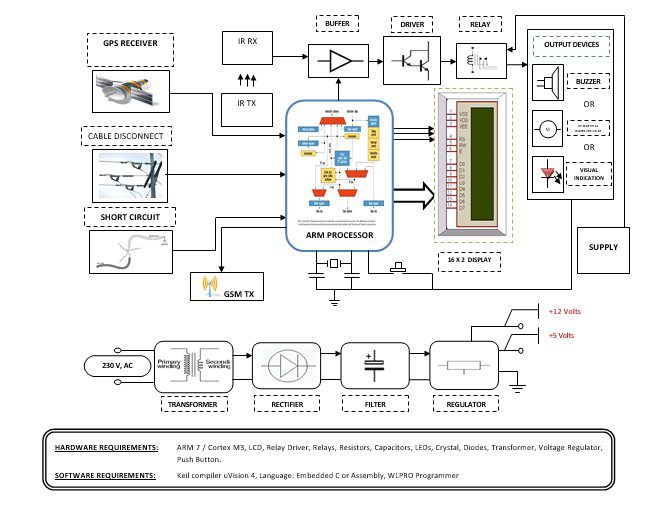
Block diagram explanation
Power supply unit
This section needs two voltages viz., +12 V & +5 V, as working voltages. Hence specially designed power supply is constructed to get regulated power supplies.
GPS module:
This is a GPS Receiver (5V Serial) with high gain having 4 Pin 2.54mm pitch strip. The third-generation POT (Patch Antenna on Top) is used by the receiver for the GPS module. It can be interfaced with normal 5V ARM7 with the help of the in-built 3V-5V converter. The interfacing is made easier with the help of a low pin count (4-pin) strip. The 4 Pins are 5V, TX, RX, and GND. This standalone 5V GPS Module does not require external components. It consists of an internal RTC Back up battery and can be directly connected to the USART of the ARM7.
The current date, time, longitude, latitude, altitude, speed, and travel direction / heading among other data, are provided by the module and can be used in many applications including navigation, fleet management, tracking systems, mapping, and robotics. The module can support up to 51 channels. The GPS solution enables small form factor devices which deliver major advancements in GPS performance, accuracy, integration, computing power, and flexibility. They are used to simplify the embedded system integration process.
GSM:
GSM Shield (SIM 900a): The SIM900 which is a complete Quad-band GSM/GPRS solution comes in a SMT module that can be embedded in customer applications. Featuring an industry-standard interface, the SIM900 delivers GSM/GPRS 850/900/1800/1900MHz performance for Data, voice, SMS, and Fax in a small form factor and with low power consumption. SIM900 can fit almost all the space requirements in the M2M application with dimensions of 24mm x 24mm x 3 mm. SIM900 is designed with a very powerful single-chip processor integrating AMR926EJ-S core. Quad-band GSM/GPRS module with a size of 24mmx24mmx3mm, SMT type suit for customer application, An embedded Powerful TCP/IP protocol stack Based upon the mature and field-proven platform, backed up by our support service, from definition to design and production.
ARM processor
ARM is a computer processor-based RISC architecture. A RISC-based computer design approach means ARM processors require significantly fewer transistors than typical processors in average computers. This approach reduces costs, heat, and power use. The low power consumption of ARM processors has made them very popular:
The ARM architecture (32-bit) is the most widely used in mobile devices, and the most popular 32-bit one in embedded systems.
Buffers
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
Drivers
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relays
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Buzzer:
A buzzer or beeper is an audio signaling device, which may be mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Typical uses of buzzers and beepers include alarm devices, timers, and confirmation of user input such as a mouse click or keystroke.
DC motor:
A DC motor relies on the fact that magnet poles repel and unlike magnetic poles attracts each other. A coil of wire with a current running through it generates an electromagnetic field aligned with the center of the coil. By switching the current on or off in a coil its magnetic field can be switched on or off or by switching the direction of the current in the coil the direction of the generated magnetic field can be switched 180°.
Indicator:
This stage provides a visual indication of which relay is actuated and deactivated, by glowing respective LED or Buzzer.
Methodology:
This project is developed to monitor and control the power grid system with GPS and GSM modules. This project contains GPS Receiver, GSM module, cable disconnect, short circuit, IR Tx and Rx, ARM controller with LCD and output. If the cable disconnect or short circuit occurs in the power grid that signal will be applied to the ARM controller and the controller will analyze the signal and activate output to indicate the short circuit or cable disconnect has occurred at the same time if a person moves around that area IR Tx and Rx captures a signal and activates a Buzzer to indicate short circuit or cable disconnect has occurred.
If anything goes wrong the Corresponding information will be sent to the Head Office via GSM Module. Location will be monitored in GPS that will send to Head Office via GSM module.
Advantages:
- Two-way communication.
- Control-technologies.
- Cost efficiency.
- Integration.
- Minimal losses.
- Security of supply
Disadvantages:
- The Power Grid relates to the electricity network only (not gas) – it concerns both distribution and transmission levels.
- Power Grids are not new “super grids”. They will not look significantly different from today’s “conventional” electricity grids, transporting and distributing power via “copper and iron” lines or cables.
Applications:
- Perform surveys of both residential and commercial energy consumption.
- Demand response system for use on the smart grid.
- Monitor systems onboard ships for safe systems operation with fewer sensors.




