Table of Contents
Introduction:


The present generation’s buzzword is “Wireless”. The Bluetooth technique, Wi-Fi, GSM’s TDMA or WLL’s CDMA, and Remote Assistance through Internet, all made life more easy and rich. The “Wireless” term releases the person from any kind of locking with the working area or concerned equipment.
The name “Wireless” only implies that the project is not controlled by land-lined lines but by the IR receivers and Transmitters. Here the Infra-Red Transmitters act as a Controlling Console and plays the key role.
The present Project implements the Wireless technique and provides the easiest automation to the railway department. This is made of two sub-projects, whose combination makes railway automation still stronger.
The second part of the Project is the “IR ID System For Railways”, which provides a unique ID to each train. When both trains run on the same track, the sensors fitted on the top of both train engines sense that another train is coming on the same track. Then both trains exchange the information and immediately stop the engine to avoid the collision, and thus the train accident will be prevented in advance.
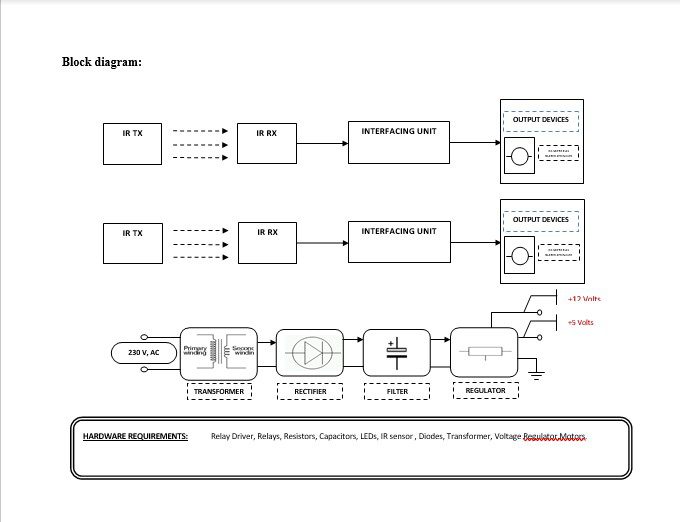

Block diagram explanation :
Power supply unit:
This section needs two voltages viz., +12 V & +5 V, as working voltages. Hence specially designed power supply is constructed to get regulated power supplies.
Buffers:
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
IR Transmitter and Receiver:
Infrared (IR) transmitters and receivers are present in many different devices, though they are most commonly found in consumer electronics. The way this technology works is that one component flashes an infrared light in a particular pattern, which another component can pick up and translate into an instruction. These transmitters and receivers are found in remote controls and all different types of devices, such as televisions and DVD players. Peripheral devices that include this technology can also allow a computer to control various other consumer electronics. Since infrared remotes are limited to line-of-sight operation, some products can be used to extend the signals over a hardwired line or radio frequency (RF) transmissions.
Drivers:
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relays:
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Indicator:
This stage provides a visual indication of which relay is actuated and deactivated, by a glowing respective LCD or Buzzer.
IR Transmitter and Receiver:
Infrared (IR) transmitters and receivers are present in many different devices, though they are most commonly found in consumer electronics. The way this technology works is that one component flashes an infrared light in a particular pattern, which another component can pick up and translate into an instruction. These transmitters and receivers are found in remote controls and all different types of devices, such as televisions and DVD players. Peripheral devices that include this technology can also allow a computer to control various other consumer electronics. Since infrared remotes are limited to line-of-sight operation, some products can be used to extend the signals over a hardwired line or radio frequency (RF) transmissions.
Methodology:
The above block diagram shows the setup “IR ID System For Railways”, which provides a unique ID to each train. When both trains run on the same track, the sensors fitted on the top of both train engines sense that another train is coming on the same track. Then both trains exchange the information and immediately stop the engine to avoid the collision, and thus the train accident will be prevented in advance.
Advantages:
- The train accident will be prevented in advance
- Fully automatic
- Low power consumption
- Low cost to design the circuit, maintenance of the circuit is good
- Easy convenience to handle.
Disadvantages:
- One-time investment cost.
- It has to be planted throughout the city.
Applications:
- Industries.
- Railways.