Table of Contents
Introduction:
Electricity is an extremely handy and useful form of energy. It plays an ever-growing role in our modern industrialized society. The electrical power systems are highly non-linear, extremely huge, and complex networks. Such electric power systems are unified for economic benefits, increased reliability, and operational advantages. They are one of the most significant elements of both national and global infrastructure, and when these systems collapse it leads to major direct and indirect impacts on the economy and national security. A power system consists of components such as generators, lines, transformers, loads, switches, and compensators. However, widely dispersed power sources and loads are the general configurations of modern power systems. Electric power systems can be divided into two sub-systems, namely, transmission systems and distribution systems. The main process of a transmission system is to transfer electric power from electric generators to the customer area, whereas a distribution system provides an ultimate link between high-voltage transmission systems and consumer services. In other words, the power is distributed to different customers from the distribution system through feeders, distributors, and service mains. Supplying electricity to consumers necessitates power generation, transmission, and distribution. Initially, electric power is generated by using electric generators such as nuclear power generators, thermal power generators, and hydraulic power generators and then transmitted through transmission systems using high voltage. Power departs from the generator and enters into a transmission substation, where huge transformers convert the generator’s voltage to extremely high voltages (155kV to 765 kV) for long-distance (up to about 300 miles) transmission. Then, the voltage level is reduced using transformers and power is transferred to customers through electric power distribution systems. Power starts from the transmission grid at distribution substations where the voltage is stepped-down (typically to less than 10kV) and carried by smaller distribution lines to supply commercial, residential, and industrial users.
Block diagram explanation
Power supply unit
This section needs two voltages viz., +12 V & +5 V, as working voltages. Hence specially designed power supply is constructed to get regulated power supplies.
LDR:
A photoresistor or light-dependent resistor (LDR) or photocell is a light-controlled variable resistor. The resistance of a photoresistor decreases with increasing incident light intensity; in other words, it exhibits photoconductivity. A photoresistor can be applied in light-sensitive detector circuits, and light- and dark-activated switching circuits.
Temperature Sensor LM 35:
LM35 is a precision IC temperature sensor with its output proportional to the temperature (in oC). The sensor circuitry is sealed and therefore it is not subjected to oxidation and other processes. With LM35, the temperature can be measured more accurately than with a thermistor. It also possesses low self-heating and does not cause more than 0.1C temperature rise in still air.
The operating temperature range is from -55°C to 150°C. The output voltage varies by 10mV in response to every oC rise/fall in ambient temperature, i.e., its scale factor is 0.01V/ oC.
Microcontroller:
The Atmel AT89 series is an Intel 8051-compatible family of 8-bit microcontrollers (µCs) manufactured by the Atmel Corporation. Based on the Intel 8051 core, the AT89 series remains very popular as general-purpose microcontrollers, due to their industry standard instruction set, and low unit cost. This allows a great amount of legacy code to be reused without modification in new applications. While considerably less powerful than the newer AT90 series of AVR RISC microcontrollers, new product development has continued with the AT89 series for the aforementioned advantages.
Buffers
Buffers do not affect the logical state of a digital signal (i.e. a logic 1 input results in a logic 1 output whereas logic 0 input results in a logic 0 output). Buffers are normally used to provide extra current drive at the output but can also be used to regularize the logic present at an interface.
Drivers
This section is used to drive the relay where the output is the complement of input which is applied to the drive but the current will be amplified.
Relays
It is an electromagnetic device that is used to drive the load connected across the relay and the o/p of the relay can be connected to the controller or load for further processing.
Methodology:
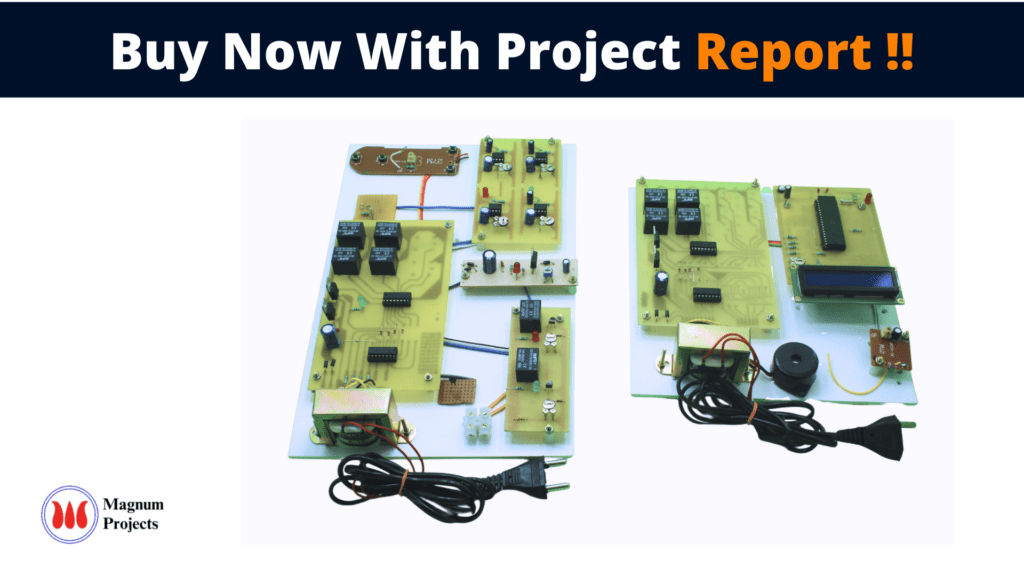
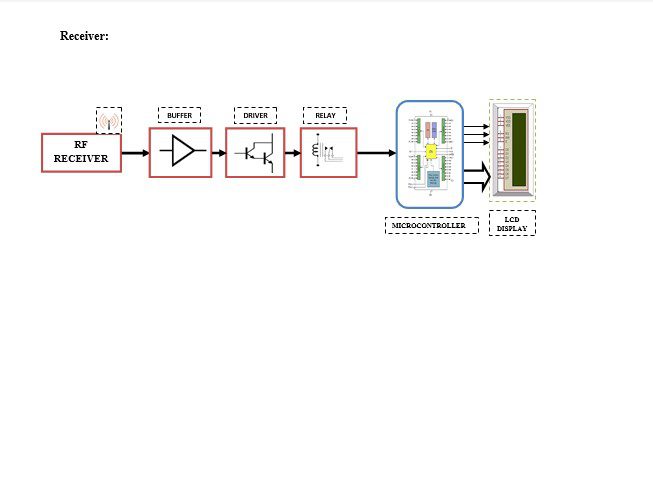
This project is developed to protect the Transformer from Over/Under Voltage, fire, and oil darkening and to send the information about the variation in Transformer to the Head Office using RF Transceiver. This project contains two sensors for oil darkening detection and temperature detection and it has a sensor to detect Over/Under Voltage occurrence detection in Transformer. After sensing that parameter the information will be transmitted to the Head Office via RF Transmitter. At the receiver end the RF Receiver receives the Transmitted signal and displays the scenario on LCD via Microcontroller. The main modules in this project are Sensors (oil darkens detection sensor and temperature sensor), a Monostable Multivibrator Microcontroller unit with LCD, an output device, and RF Transceiver.
Advantages:
1. Provides alerts to protect the transformer from high temperature and oil darkening.
2. In this project losses are Minimal.
3. This project can implement for the Security of supply.
Disadvantages:
1. The electricity network only (not gas) concerns both distribution and transmission levels.
2. It increases the cost whereas digital systems reduce the cost of the system.
Applications:
- This system can be implemented in industries.
- This system can be implanted in schools, colleges, companies, etc…
- This system can be used to monitor and control the home appliances